HSE Scientists Discover How to Predict Charitable Behaviour Through Physiological Reactions
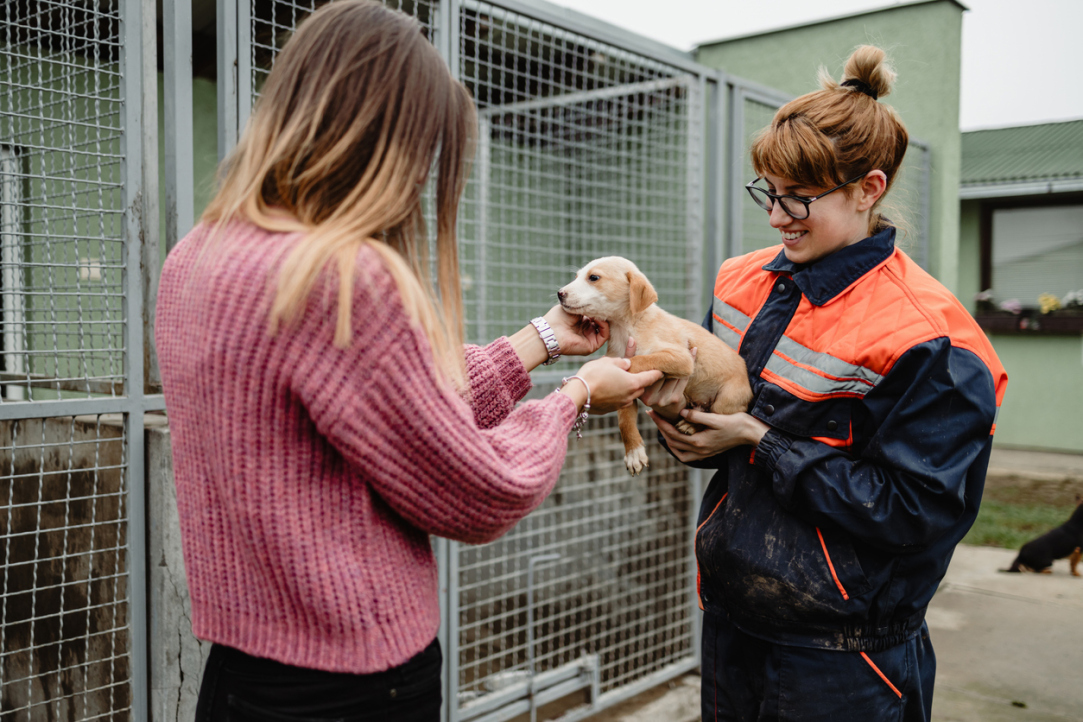

Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have investigated how the emotional impact of advertising affects the amount people willing to donate to support animal welfare. To accomplish this, the researchers measured physiological responses such as heart rate, electrodermal activity, and facial expressions in individuals viewing various photos of dogs. The findings indicate that willingness to donate is most accurately predicted by heart rate and facial muscle activation. The study has been published in Social Psychology.
Neuromarketing techniques, which assess audience emotional responses and engagement based on physiological and neural activity, are widely used to evaluate the effectiveness of commercial advertising. However, these techniques are only just beginning to be applied in predicting the success of charitable giving appeals. This type of message is particularly well-suited for neuromarketing approaches, since the decision to donate is often driven by emotions, sometimes without the donor's conscious awareness. In this context, objective methods of assessing emotional states through physiological indicators can uncover subconscious audience reactions, which traditional surveys are unable to detect.
The scientific literature presents conflicting evidence regarding the impact of emotions on donations. This is largely due to methodological limitations, as most previous studies relied on declarative methods, such as surveys and rating scales, where respondents self-reported their feelings. However, study participants are not always able to accurately identify the emotions evoked by charity advertising, or may be unwilling to openly share them, especially when the fundraising goals involve controversial or taboo topics, such as supporting socially marginalised groups. One such topic is the rescue of stray animals.
‘The attitude toward stray dogs in society is mixed; some view them as victims of circumstance, while others see them as a threat. Based on this, we hypothesised that using neuromarketing methods to study the relationship between emotions and charitable behaviour would be particularly relevant in the context of helping these animals,' explains Anna Shepelenko, co-author of the study, Research Fellow at the Centre for Cognition and Decision Making of the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience, and participant in the project 'I Choose to Pursue Science,' implemented with support from the Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education.
To explore the potential of using neuromarketing methods to evaluate the effectiveness of charitable appeals, Anna Shepelenko, Vladimir Kosonogov, and Anna Shestakova, Research Fellows at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience, conducted an experiment that comprehensively analysed the relationship between physiological reactions and the motivation to donate. During the experiment, 54 volunteers were shown 32 photos of dogs. After viewing each photo, participants had the option to donate a portion of the money they received for participating in the experiment to support the animal shown. All donations were real, and participants were informed of this in advance. The funds raised were donated to the Giving Hope Fund for homeless pets. Additionally, participants were asked to rate how pleasant or unpleasant they felt about the image and how aroused they were.
During the presentation of the images, the researchers recorded three physiological indicators: heart rate, skin conductance, and facial muscle activity. These indicators enabled the researchers to capture objective signs of emotional states and compare them with the participants' self-reported feelings.
The researchers found a correlation between heart rate, facial muscle movement, and the amount of donations. Unpleasant images that evoked strong emotions caused a greater decrease in heart rate compared to pleasant and neutral ones, and the lower the heart rate, the larger the donation participants were willing to make. Most of the funds were raised by photos that activated the viewer's corrugator supercilii, the muscle responsible for furrowing the brow, which is associated with unpleasant emotions. In contrast, animals whose appearance evoked pleasant emotions, associated with the activity of the zygomaticus major muscle involved in smiling, elicited the smallest donations.
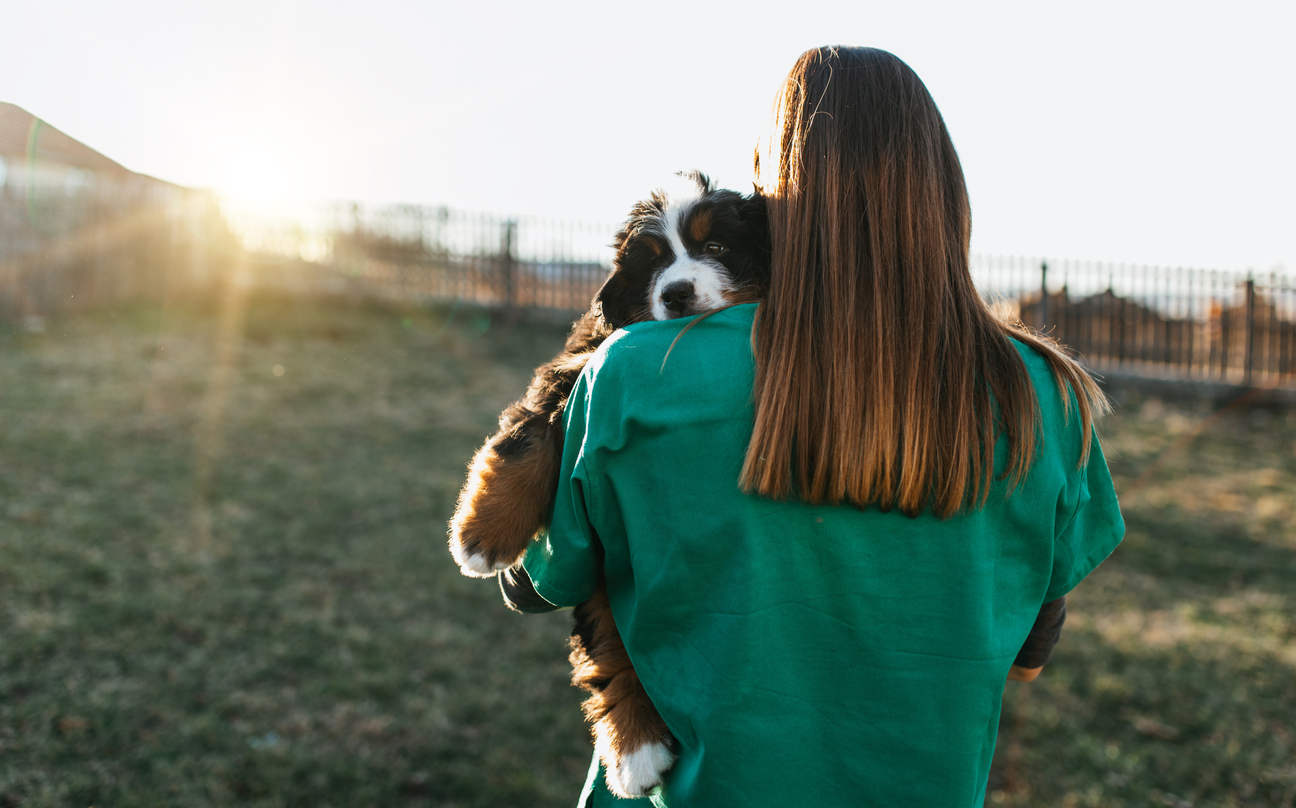

Additionally, the researchers examined how various characteristics of the prospective beneficiaries, such as the animal's age, health, visible signs of being a stray, and the presence of a potential caregiver, might influence donors' emotions and the size of their donations. To this end, the animals in the photographs were shown in various conditions—healthy or sick, domestic or stray, as puppies or adults, and with or without a human nearby. Photos of healthy, domestic dogs proved to be the least effective in soliciting donations, raising the smallest amounts. The researchers' hypothesis that pictures of puppies would elicit the greatest response was not confirmed; the difference in donations between puppies and adult dogs was insignificant. The presence of a human next to an animal also had no impact on charitable behaviour.
'Our findings demonstrate that neuromarketing methods can be a reliable tool for evaluating the effectiveness of charity advertising. Given the ambivalence of society's attitudes toward stray animals, we anticipated some discrepancies between the self-reported emotional data and the physiological reactions measured, but this was not the case. In other words, we found no evidence that the participants were attempting to conceal their true emotions toward the dogs. In the context of a laboratory experiment, participants preferred to donate to animals that evoked strong and unpleasant emotions, as confirmed by both self-reported data and physiological reactions,' according to Anna Shepelenko.
At the same time, she emphasises that the results do not account for the potential effect of avoiding negative information, which may occur with repeated exposure to upsetting content. Therefore, to further study the influence of emotions on prosocial behaviour, additional research is needed that examines donor behaviour over an extended period.
See also:
AI to Enable Accurate Modelling of Data Storage System Performance
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science have developed a new approach to modelling data storage systems based on generative machine learning models. This approach makes it possible to accurately predict the key performance characteristics of such systems under various conditions. Results have been published in the IEEE Access journal.
Researchers Present the Rating of Ideal Life Partner Traits
An international research team surveyed over 10,000 respondents across 43 countries to examine how closely the ideal image of a romantic partner aligns with the actual partners people choose, and how this alignment shapes their romantic satisfaction. Based on the survey, the researchers compiled two ratings—qualities of an ideal life partner and the most valued traits in actual partners. The results have been published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Trend-Watching: Radical Innovations in Creative Industries and Artistic Practices
The rapid development of technology, the adaptation of business processes to new economic realities, and changing audience demands require professionals in the creative industries to keep up with current trends and be flexible in their approach to projects. Between April and May 2025, the Institute for Creative Industries Development (ICID) at the HSE Faculty of Creative Industries conducted a trend study within the creative sector.
From Neural Networks to Stock Markets: Advancing Computer Science Research at HSE University in Nizhny Novgorod
The International Laboratory of Algorithms and Technologies for Network Analysis (LATNA), established in 2011 at HSE University in Nizhny Novgorod, conducts a wide range of fundamental and applied research, including joint projects with large companies: Sberbank, Yandex, and other leaders of the IT industry. The methods developed by the university's researchers not only enrich science, but also make it possible to improve the work of transport companies and conduct medical and genetic research more successfully. HSE News Service discussed work of the laboratory with its head, Professor Valery Kalyagin.
Children with Autism Process Sounds Differently
For the first time, an international team of researchers—including scientists from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain—combined magnetoencephalography and morphometric analysis in a single experiment to study children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). The study found that children with autism have more difficulty filtering and processing sounds, particularly in the brain region typically responsible for language comprehension. The study has been published in Cerebral Cortex.
HSE Scientists Discover Method to Convert CO₂ into Fuel Without Expensive Reagents
Researchers at HSE MIEM, in collaboration with Chinese scientists, have developed a catalyst that efficiently converts CO₂ into formic acid. Thanks to carbon coating, it remains stable in acidic environments and functions with minimal potassium, contrary to previous beliefs that high concentrations were necessary. This could lower the cost of CO₂ processing and simplify its industrial application—eg in producing fuel for environmentally friendly transportation. The study has been published in Nature Communications.
HSE Scientists Reveal How Staying at Alma Mater Can Affect Early-Career Researchers
Many early-career scientists continue their academic careers at the same university where they studied, a practice known as academic inbreeding. A researcher at the HSE Institute of Education analysed the impact of academic inbreeding on publication activity in the natural sciences and mathematics. The study found that the impact is ambiguous and depends on various factors, including the university's geographical location, its financial resources, and the state of the regional academic employment market. A paper with the study findings has been published in Research Policy.
Group and Shuffle: Researchers at HSE University and AIRI Accelerate Neural Network Fine-Tuning
Researchers at HSE University and the AIRI Institute have proposed a method for quickly fine-tuning neural networks. Their approach involves processing data in groups and then optimally shuffling these groups to improve their interactions. The method outperforms alternatives in image generation and analysis, as well as in fine-tuning text models, all while requiring less memory and training time. The results have been presented at the NeurIPS 2024 Conference.
When Thoughts Become Movement: How Brain–Computer Interfaces Are Transforming Medicine and Daily Life
At the dawn of the 21st century, humans are increasingly becoming not just observers, but active participants in the technological revolution. Among the breakthroughs with the potential to change the lives of millions, brain–computer interfaces (BCIs)—systems that connect the brain to external devices—hold a special place. These technologies were the focal point of the spring International School ‘A New Generation of Neurointerfaces,’ which took place at HSE University.
New Clustering Method Simplifies Analysis of Large Data Sets
Researchers from HSE University and the Institute of Control Sciences of the Russian Academy of Sciences have proposed a new method of data analysis: tunnel clustering. It allows for the rapid identification of groups of similar objects and requires fewer computational resources than traditional methods. Depending on the data configuration, the algorithm can operate dozens of times faster than its counterparts. Thestudy was published in the journal Doklady Rossijskoj Akademii Nauk. Mathematika, Informatika, Processy Upravlenia.