Biologists at HSE University Warn of Potential Errors in MicroRNA Overexpression Method
Researchers at HSE University and the RAS Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry have discovered that a common method of studying genes, which relies on the overexpression of microRNAs, can produce inaccurate results. This method is widely used in the study of various pathologies, in particular cancers. Errors in experiments can lead to incorrect conclusions, affecting the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. The study findings have been published in BBA.
The work of a researcher involves not only continuous pursuit of new discoveries but also careful attention to conventional, established knowledge. Sometimes, reliable and seemingly proven methods have characteristics that were previously overlooked.
A group of researchers led by Alexander Tonevitsky, Dean of the Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology at HSE University, have discovered such characteristics in the microRNA overexpression method. The scientists found that, in some cases, the results of experiments using this method may be incorrect, and these errors are very difficult to detect.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNA molecules, approximately 20 to 25 nucleotides in length. They play an important role in regulating gene expression by determining how much protein will be synthesised in a cell from a specific molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). This regulation is facilitated by a short fragment within the miRNA, which can bind to the target mRNA molecule if it finds a reverse complement (biologically compatible) sequence. When this occurs, protein synthesis from the mRNA is halted, leading to a decrease in gene expression.
As diseases, including cancers, progress, changes in microRNA expression levels are observed. Specifically, in prostate cancer, the number of miR-93-5p microRNAs increases, and higher levels of their expression are associated with greater aggressiveness of the disease. By significantly increasing the number of miRNA in laboratory cells, researchers can gain a clearer understanding of the processes associated with elevated expression of this miRNA.
A common approach for miRNA overexpression involves initially increasing the amount of precursor RNA in cells—a longer molecule from which miRNA is subsequently generated through cleavage by the Dicer enzyme. This is a natural process for the cell. However, the sequence of miRNAs formed as a result depends on how accurately the Dicer enzyme cleaves the precursor molecule.
The authors of the paper studied how the Dicer enzyme cleaves the molecule. They encoded the desired sequence in the precursor molecule, anticipating that Dicer would accurately cleave it as intended. However, it turned out that Dicer does not always operate as scientists expect. The enzyme primarily functions like a molecular ruler, consistently measuring a length of 22 nucleotides. During the synthesis of the precursor molecule, one or more uracils (a nucleotide base unique to RNA) are typically added to the end of the sequence. As a result, if a given miRNA sequence is longer than 19 nucleotides, the added uracils cause Dicer to cleave the molecule at an unintended location. This shift leads to the formation of miRNA isoforms.
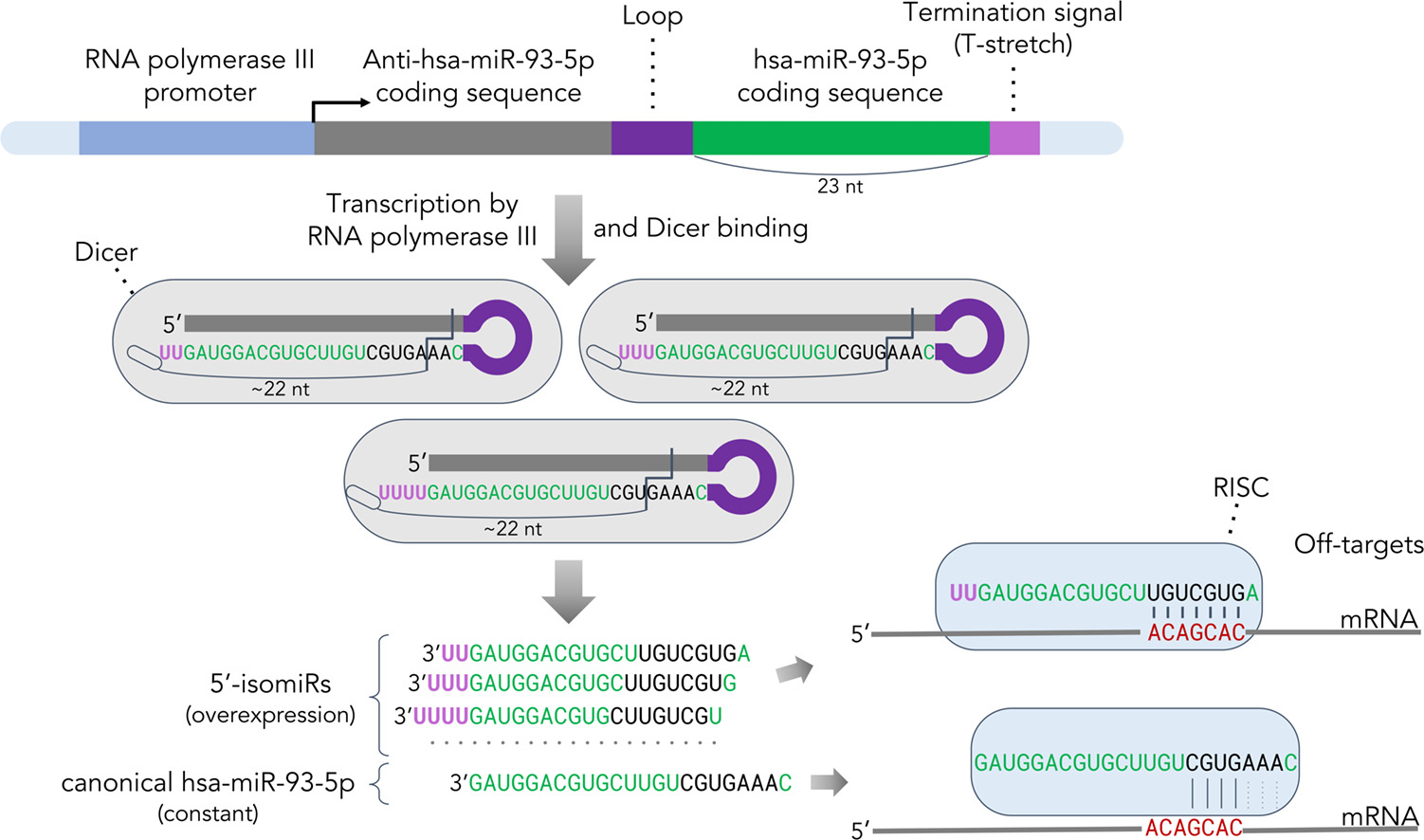
To investigate the cause of the shift in cleavage position of the precursor molecule, the scientists experimentally set several miRNA sequences of varying lengths, including a 23-nucleotide chain corresponding to the miR-93-5p miRNA. Using sequencing—a method that fully deciphers the nucleotide sequence of RNA or DNA molecules—the scientists observed that the added uracils in chains longer than 19 nucleotides cause a shift in the cleavage position.

Diana Maltseva
The formation of miR-93-5p miRNA isoforms resulted in a decrease in the expression of the HMGA1 gene, which plays a role in disrupting genetic information transmission during cell division and in regulating gene expression. However, HMGA1 was not the target of the standard form of miR-93-5p. Without knowledge of miRNA isoform formation, one might draw incorrect conclusions about the molecular mechanisms of the studied miRNA in prostate cancer.
'Isoforms may target the wrong mRNA molecules instead of those intended in the experiment, leading to the suppression of unintended genes. Understanding this peculiarity is crucial for both basic research and medical applications,' according to Diana Maltseva, Head of the International Laboratory of Microphysiological Systems at HSE University.
Scientists worldwide use the miRNA overexpression method in their experiments. Typically, the accuracy of the results is verified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). However, this method was not sufficiently sensitive in this case.
'Our study has shown that only sequencing can reveal the shift in the cleavage position. Unfortunately, sequencing is a relatively expensive method, and not all laboratories can afford it. Therefore, it is crucial to develop new methods for miRNA overexpression and to design experiments carefully,' Maltseva comments.
See also:
Scientists Develop AI Tool for Designing Novel Materials
An international team of scientists, including researchers from HSE University, has developed a new generative model called the Wyckoff Transformer (WyFormer) for creating symmetrical crystal structures. The neural network will make it possible to design materials with specified properties for use in semiconductors, solar panels, medical devices, and other high-tech applications. The scientists will present their work at ICML, a leading international conference on machine learning, on July 15 in Vancouver. A preprint of the paper is available on arxiv.org, with the code and data released under an open-source license.
HSE Linguists Study How Bilinguals Use Phrases with Numerals in Russian
Researchers at HSE University analysed over 4,000 examples of Russian spoken by bilinguals for whom Russian is a second language, collected from seven regions of Russia. They found that most non-standard numeral constructions are influenced not only by the speakers’ native languages but also by how frequently these expressions occur in everyday speech. For example, common phrases like 'two hours' or 'five kilometres’ almost always match the standard literary form, while less familiar expressions—especially those involving the numerals two to four or collective forms like dvoe and troe (used for referring to people)—often differ from the norm. The study has been published in Journal of Bilingualism.
Overcoming Baby Duck Syndrome: How Repeated Use Improves Acceptance of Interface Updates
Users often prefer older versions of interfaces due to a cognitive bias known as the baby duck syndrome, where their first experience with an interface becomes the benchmark against which all future updates are judged. However, an experiment conducted by researchers from HSE University produced an encouraging result: simply re-exposing users to the updated interface reduced the bias and improved their overall perception of the new version. The study has been published in Cognitive Processing.
Mathematicians from HSE Campus in Nizhny Novgorod Prove Existence of Robust Chaos in Complex Systems
Researchers from the International Laboratory of Dynamical Systems and Applications at the HSE Campus in Nizhny Novgorod have developed a theory that enables a mathematical proof of robust chaotic dynamics in networks of interacting elements. This research opens up new possibilities for exploring complex dynamical processes in neuroscience, biology, medicine, chemistry, optics, and other fields. The study findings have been accepted for publication in Physical Review Letters, a leading international journal. The findings are available on arXiv.org.
Mathematicians from HSE University–Nizhny Novgorod Solve 57-Year-Old Problem
In 1968, American mathematician Paul Chernoff proposed a theorem that allows for the approximate calculation of operator semigroups, complex but useful mathematical constructions that describe how the states of multiparticle systems change over time. The method is based on a sequence of approximations—steps which make the result increasingly accurate. But until now it was unclear how quickly these steps lead to the result and what exactly influences this speed. This problem has been fully solved for the first time by mathematicians Oleg Galkin and Ivan Remizov from the Nizhny Novgorod campus of HSE University. Their work paves the way for more reliable calculations in various fields of science. The results were published in the Israel Journal of Mathematics (Q1).
Large Language Models No Longer Require Powerful Servers
Scientists from Yandex, HSE University, MIT, KAUST, and ISTA have made a breakthrough in optimising LLMs. Yandex Research, in collaboration with leading science and technology universities, has developed a method for rapidly compressing large language models (LLMs) without compromising quality. Now, a smartphone or laptop is enough to work with LLMs—there's no need for expensive servers or high-powered GPUs.
AI to Enable Accurate Modelling of Data Storage System Performance
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science have developed a new approach to modelling data storage systems based on generative machine learning models. This approach makes it possible to accurately predict the key performance characteristics of such systems under various conditions. Results have been published in the IEEE Access journal.
Researchers Present the Rating of Ideal Life Partner Traits
An international research team surveyed over 10,000 respondents across 43 countries to examine how closely the ideal image of a romantic partner aligns with the actual partners people choose, and how this alignment shapes their romantic satisfaction. Based on the survey, the researchers compiled two ratings—qualities of an ideal life partner and the most valued traits in actual partners. The results have been published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Trend-Watching: Radical Innovations in Creative Industries and Artistic Practices
The rapid development of technology, the adaptation of business processes to new economic realities, and changing audience demands require professionals in the creative industries to keep up with current trends and be flexible in their approach to projects. Between April and May 2025, the Institute for Creative Industries Development (ICID) at the HSE Faculty of Creative Industries conducted a trend study within the creative sector.
From Neural Networks to Stock Markets: Advancing Computer Science Research at HSE University in Nizhny Novgorod
The International Laboratory of Algorithms and Technologies for Network Analysis (LATNA), established in 2011 at HSE University in Nizhny Novgorod, conducts a wide range of fundamental and applied research, including joint projects with large companies: Sberbank, Yandex, and other leaders of the IT industry. The methods developed by the university's researchers not only enrich science, but also make it possible to improve the work of transport companies and conduct medical and genetic research more successfully. HSE News Service discussed work of the laboratory with its head, Professor Valery Kalyagin.